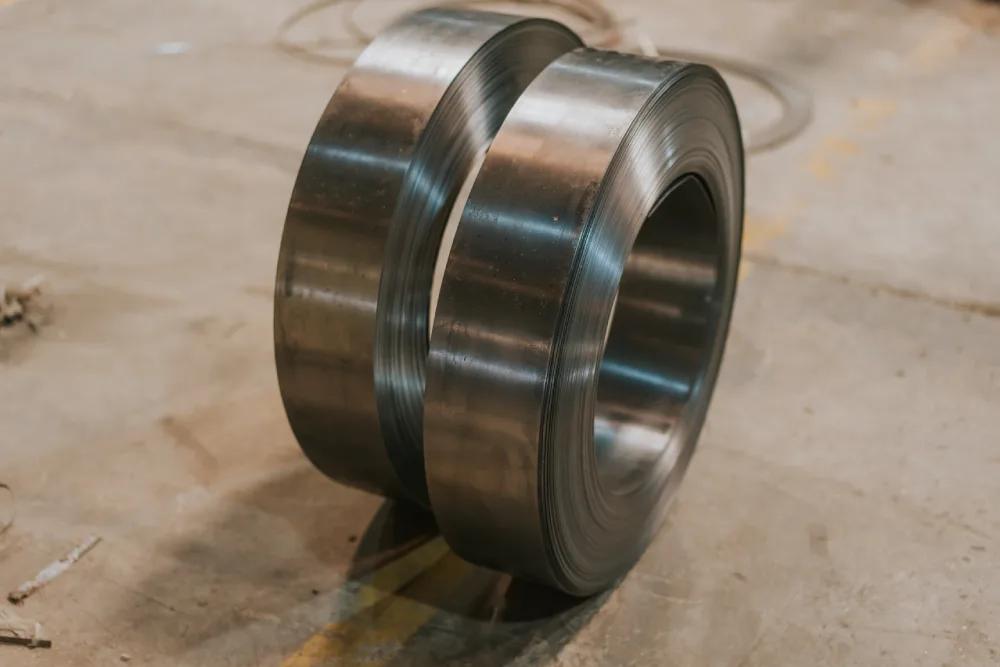
Cold Rolled Steel Strips
Description
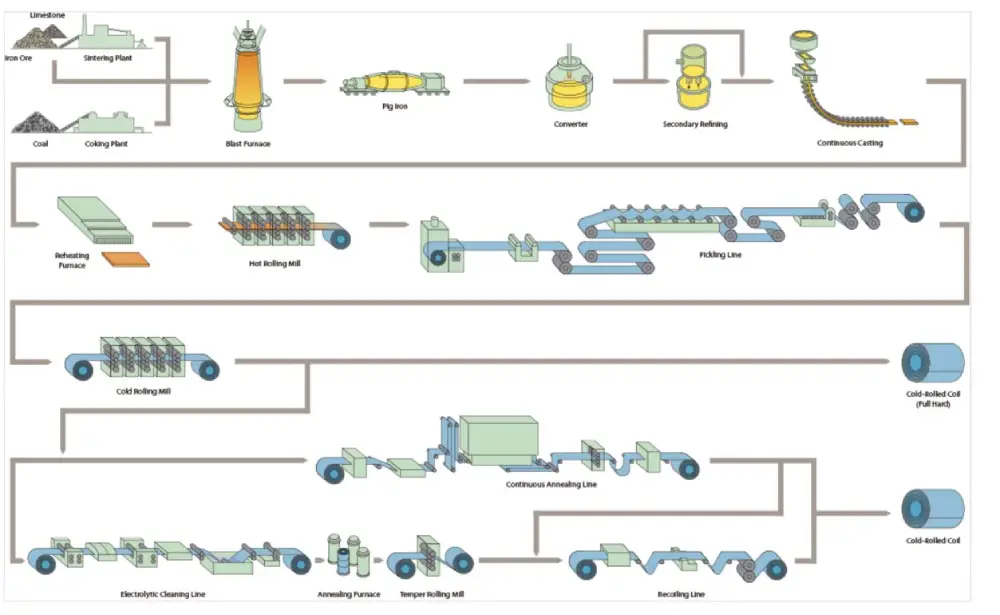
1. Material Selection and Preparation:
- Start with a coil or sheet of carbon steel, typically in the form of hot-rolled coil or sheet
2. Pickling:
- Surface cleaning with acid to remove any contaminants, scale, or oxides that may have formed during storage or previous processing steps.
3. Cold Rolling:
- The cleaned steel strip is fed into a series of rolling mills
- Each pass through the rolling mill reduces the thickness of the steel while increasing its length.
- The steel strip is subjected to pressure between rollers to deform it into the desired thickness and shape.
- Cold rolling is typically performed at room temperature or slightly below to improve the material’s strength and hardness.
4. Annealing (Optional):
- After cold rolling, the steel may undergo an optional annealing process to relieve internal stresses and improve ductility.
- Annealing may involve heating the steel to a specific temperature and then gradually cooling it down in a controlled environment.
5. Skin Pass (Optional):
- In some cases, a skin pass or temper rolling process may be performed after cold rolling to improve surface finish and remove any remaining surface imperfections.
- This process involves passing the cold-rolled strip through a set of rollers with a very light reduction in thickness.
6. Trimming and Slitting
- Trim irregular edges and ensure uniform width of the cold-rolled strip.
- Slit the cold-rolled strip into narrower coils or sheets, if required, using slitting machines.
7. Inspection and Quality Control:
- Perform visual and dimensional inspections to ensure the cold-rolled steel meets specified quality standards.
- Check for defects, thickness uniformity, and surface finish.
Applications
Carbon steel strips, especially those produced through cold rolling processes, find diverse
applications across various industries due to their versatility, strength, and formability. Here
are some common applications:
- Automotive Industry: Carbon steel strips are widely used in automotive manufacturing for producing components such as brackets, circlips, clamps, springs, washers, safety seat belts, clutch, brakes, and reinforcement plates due to their high strength, formability, and cost-effectiveness.
- Construction: Carbon steel strips are utilized in the construction industry for various applications, including framing, bracing, reinforcement, and support structures. They are commonly used in the manufacture of studs, tracks, purlins, and other structural components due to their strength, durability, and ease of fabrication.
- Consumer Goods: Carbon steel strips are employed in the production of a wide range of consumer goods such as shoes, safety shoes, appliances, furniture, kitchenware, and utensils. They are used for making components like hinges, handles, brackets, and decorative trim due to their strength, formability, and ability to maintain a smooth surface finish.
- Electronics: Carbon steel strips are used in the electronics industry for manufacturing components such as battery contacts, springs, connectors, and shielding due to their electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, and formability.
- Industrial Machinery: Carbon steel strips find application in the manufacturing of industrial machinery and equipment such as conveyor systems, machine frames, tooling, and stamping dies due to their strength, toughness, and machinability.
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): Carbon steel strips are used in the HVAC industry for manufacturing components such as ductwork, false ceilings, air handling units, and heat exchangers due to their strength, corrosion resistance, and compatibility with HVAC system requirements.
C98
C80
C75
C70
C67S
C65
C62
C60
C55
C45
SK5
51CrV4
SK2M-R(CR4)
C98
| Grade | C98 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 2.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, EN, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1098 | C98 / CK98 | EN44D | S98C | C98 |
|---|
| 98C6 / C98 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 200 Max | 25 Min | 690 Max | 310 Min |
| 98C6 / C98 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.90 – 1.05 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.05 Max | 0.05 Max |
C80
| Grade | C80 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | EN42J | C80 / CK80 | S80C | 80C6 | SAE 1080/AISI 1080 | HC14 | HC80 |
|---|
| 80C6 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 220 Max | 25 Min | 640 Max | 290 Min |
| 80C6 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.75 – 0.85 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.050 Max | 0.050 Max |
| 85C6 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 220 Max | 25 Min | 640 Max | 290 Min |
| 85C6 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.80 – 0.90 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.050 Max | 0.050 Max |
C75
| Grade | C75 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1075 | C75 / CK75 | S75C | C75 / CK75 |
|---|
| 75C6 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 220 Max | 25 Min | 640 Max | 290 Min |
| 75C6 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.70 – 0.80 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.050 Max | 0.050 Max |
| C75S | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 200 Max | 15 Min | 640 Max | 510 Max |
| C75S | Chemical Composition % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum |
| 0.70 – 0.80 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.15 – 0.35 | 0.025 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.10 Max |
C70
| Grade | C70 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1070 | C70 / CK70 | S70C | C70 / CK70 |
|---|
| 70C6 / C70 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 215 Max | 30 Min | 590 Max | 270 Min |
| 70C6 / C70 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.65 – 0.75 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.050 Max | 0.050 Max |
C67S
| Grade | C67S |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | EN |
| Equivalent Grades | – | – | – | – |
|---|
| C67S | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 200 Max | 16 Min | 640 Max | 510 Max |
| C67S | Chemical Composition % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum |
| 0.65 – 0.73 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.15 – 0.35% | 0.025 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.10 Max |
C65
| Grade | C65 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, EN, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1065 | C65 / CK65 | EN43D | S60C | C65 |
|---|
| C65 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 205 Max | 30 Min | 590 Max | 270 Min |
| C65 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.60 – 0.69 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.05 Max | 0.05 Max |
C62
| Grade | C62 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, EN, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1062 | C62 / CK62 | EN43D | S60C | C62 |
|---|
| C62 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 200 Max | 30 Min | 590 Max | 270 Min |
| C62 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.57 – 0.67 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max |
C60
| Grade | C60 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, EN, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1060 | C60 / CK60 | EN43D | S60C / S58C / SUP11A | C60 |
|---|
| C60 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 200 HV Max | 30 Min | 590 Max | 270 Min |
| C60 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.55 – 0.65 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max |
C55
| Grade | C55 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, EN, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | C55E | C55 / CK55 | EN9 | C55 / CK55 | SAE 1055 |
|---|
| C55 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 195 Max | 30 Min | 590 Max | 270 Min |
| C55 | Chemical Composition % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum |
| 0.50 – 0.60 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.40 | 0.045 | 0.045 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.10 |
| C55S | Chemical Composition % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 185 HV Max | 17 Min | 600 Max | 480 Max |
| C55S | Chemical Composition % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum |
| 0.52 – 0.60 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.15 – 0.35 | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.40 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.10 Max |
C45
| Grade | C45 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 8.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright, Matte |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | EN, JIS, SPAIN UNE, IS |
| Equivalent Grades | C45E | S45C | C45K | 45C8 |
|---|
| C45 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 185 Max | 30 Min | 590 Max | 270 Min |
| C45 | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.40 – 0.50 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.10 -0.35 | 0.05 Max | 0.05 Max |
| C45E | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 180 Max | 18 Min | 570 Max | 455 Max |
| C45E | Chemical Composition % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum |
| 0.42 – 0.50 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.40 Max | 0.035 Max | 0.035 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.10 Max |
SK5
| Grade | SK5 (SK85) |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | JIS G 4401, SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, JIS |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 1086 | C80W1 | SK5 / SK85 |
|---|
| SK5 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 200 Max | 25 | 685 Max | 310 Min |
| SK5 | Chemical Composition % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium |
| 0.80 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.50 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.03 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.25 Max | 0.30 Max |
51CrV4
| Grade | 50CrV4 / 51CrV4 |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.30 – 5.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Bright |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | SAE / AISI, DIN- GERMANY, EN, JIS, UNI |
| Equivalent Grades | SAE 6150 | 50CrV4 | EN47 / 735A50 | SUP10 | 50CrV4 |
|---|
| 51CrV4 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 220 Max | 13 Min | 700 Max | 550 Max |
| 51CrV4 | Chemical Composition % | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Molybdenum | Vanadium |
| 0.47 – 0.55 | 0.70 – 1.10 | 0.40 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.40 Max | 0.90 – 1.20 | 0.10 Max | 0.10 – 0.25 |
| EN47 / 50Cr4 | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 240 Max | 20 Min | 780 Max | 340 Min |
| EN47 / 50Cr4 | Chemical Composition % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Chromium | Vanadium |
| 0.45 – 0.55 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.050 Max | 0.050 Max | 0.90 – 1.20 | – |
SK2M-R(CR4)
| Grade | SK2M-R(CR4) |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 0.40 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | – |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 50.00 |
| Finish | Bright |
| Edges | Sheared Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 0.40 |
| Standards | JIS |
| Equivalent Grades | – | – | – | – | – |
|---|
| SK2M-R(CR4) | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HBW) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) Mpa | Yield Strength (N/mm²) Mpa |
| 424 | 34 | 845 Min | 699 Min |
| SK2M-R(CR4) | Chemical Composition % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium | Copper |
| 1.1 – 1.3 | 0.50 Max | 0.35 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.25 Max | 0.20 – 0.50 | 0.25 Max |







 ISO 9001:2015Brochure
ISO 9001:2015Brochure