Hardened and Tempered steel strips
Description
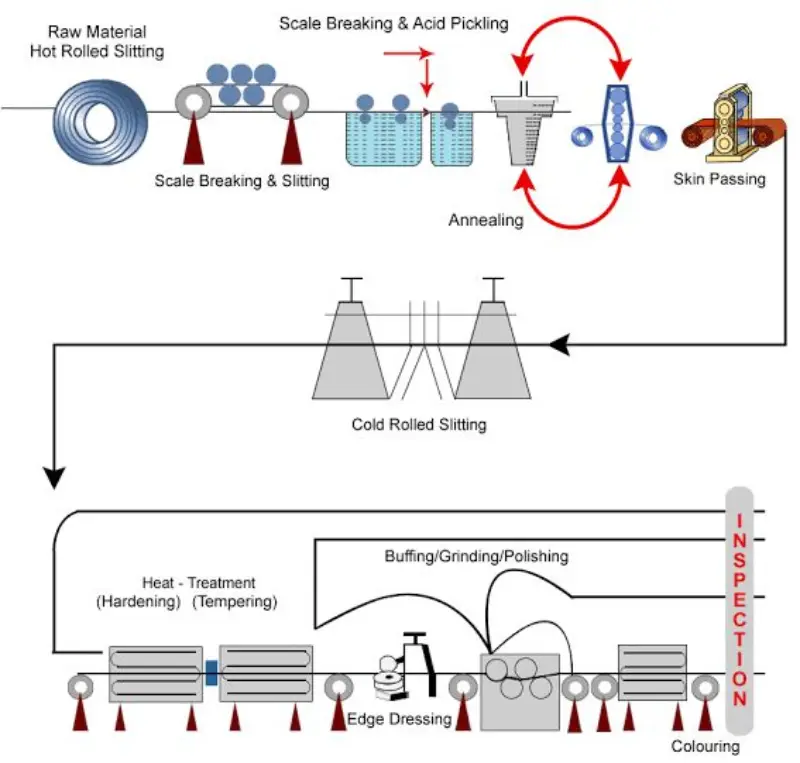
Additional Process steps for H&T Strips
- Heat Treatment (Hardening): The cold-rolled steel strip is then subjected to a heat treatment process known as hardening. This involves heating the steel to a critical temperature, typically above its austenitizing temperature, and then rapidly quenching it in a quenching medium such as oil or water. Rapid quenching causes the steel to undergo a phase transformation, forming a hardened structure with increased hardness and strength.
- Tempering: The hardened steel strip is then tempered to achieve the desired balance of hardness and toughness. Tempering involves reheating the hardened steel to a specific temperature below its critical temperature and holding it for a precise duration. This process relieves some of the internal stresses introduced during hardening and allows controlled transformation of the martensitic structure, resulting in a tougher and more ductile material.
- Finishing Operations: After hardening and tempering, the steel strip may undergo various finishing operations such as straightening, grinding, or polishing to achieve the final dimensions, surface finish, and edge profile required for the intended
application.
Applications
- Hardened and tempered steel strips: which undergo specific heat treatment processes to achieve desired mechanical properties, find various applications across industries where durability, strength, and precision are crucial. Here are some common applications:
- Cutting Tools: Hardened and tempered steel strips are widely used in the production of cutting tools such as knives, blades, saws, and shears due to their high hardness, wear resistance, and edge retention properties.
- Industrial Springs: These steel strips are employed in the manufacturing of industrial springs, including coil springs, flat springs, and leaf springs, used in automotive, machinery, and aerospace applications due to their excellent elastic modulus, fatigue
resistance, and durability. - Textile Machinery: Hardened and tempered steel strips are utilized in textile machinery for producing components such as reeds, heddles, shuttles, and picker sticks due to their high tensile strength, wear resistance, and dimensional stability.
- Hand Tools: These steel strips are used in the production of hand tools such as screwdrivers, wrenches, chisels, and punches due to their hardness, toughness, and resistance to deformation under high loads.
- Automotive Components: Hardened and tempered steel strips find application in automotive manufacturing for producing various components such as clutch plates, brake components, transmission parts, and engine valves due to their strength, durability, and wear resistance.
- Medical Instruments: They are used in the production of surgical instruments and medical devices due to their corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, and ability to maintain sharp edges.
- Woodworking Tools: Hardened and tempered steel strips are utilized in the production of woodworking tools such as plane irons, chisels, gouges, and saw blades due to their hardness, sharpness, and wear resistance.
- Measuring Instruments: These steel strips are employed in the production of precision measuring instruments such as rulers, calipers, micrometers, and gauges due to their dimensional stability, accuracy, and resistance to deformation.
- Electrical Components: Hardened and tempered steel strips find application in the electrical industry for producing components such as springs, contacts, and connectors due to their conductivity, resilience, and durability.
- Construction: Hand Trowels, machine trowels, painting equipment
- Gardening Tools: Brush cutter blades, lawn mower blade
- Sporting Goods: They are used in the manufacturing of sporting goods such as knives, swords, bows, and arrows, as well as components for bicycles, golf clubs, and firearms due to their strength, hardness, and impact resistance.
C98
C80
C62
SK5
51CrV4
C98
| Grade | C98 H&T |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 2.50 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 Max |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Grey, Bright, Blue, Bronze |
| Edges | Sheared Edge, Round Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | – |
| C98 H&T | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 35 – 55 | 6 Min | 1570 – 1760 | 1470 Min |
| C98 H&T | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.90 – 1.05 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.05 Max | 0.05 Max |
C80
| Grade | C80 H&T |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 3.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 Max |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Grey, Bright, Blue, Bronze |
| Edges | Sheared Edge, Round Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | – |
| C80 H&T | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 35 – 55 | 6 Min | 1180 – 1570 | 1080 Min |
| C80 H&T | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.75 – 0.85 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.35 Max | 0.025 Max | 0.025 Max |
C62
| Grade | C62 H&T |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 2.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Grey, Bright, Blue, Bronze |
| Edges | Sheared Edge, Round Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | – |
| C62 H&T | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 35 – 55 | 6 Min | 1180 – 1420 | 1030 Min |
| C62 H&T | Chemical Composition % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous |
| 0.57 – 0.67 | 0.60 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.04 Max | 0.04 Max |
SK5
| Grade | SK5 (SK85) H&T |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 3.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 Max |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Grey, Bright, Blue, Bronze |
| Edges | Sheared Edge, Round Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | – |
| SK5 H&T | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HRC) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 35 – 55 | 6 Min | 1570 – 1760 | 1470 Min |
| SK5 H&T | Chemical Composition % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Nickel | Chromium |
| 0.80 – 0.90 | 0.10 – 0.50 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.03 Max | 0.03 Max | 0.25 Max | 0.30 Max |
51CrV4
| Grade | 50CrV4 / 51CrV4 H&T |
|---|---|
| Thickness (mm) | 0.10 – 3.00 |
| Full Width Range (mm) | 300 – 400 |
| Slit Width (mm) | 6.00 – 250 |
| Finish | Grey, Bright, Blue, Bronze |
| Edges | Sheared Edge, Round Edge |
| Slitting Thickness (mm) | 0.20 – 2.50 |
| Standards | – |
| 50CrV4 H&T | Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (HV) | Elongation % | Tensile Strength (N/mm²) | Yield Strength (N/mm²) |
| 55 Max | 4 Min | 1880 – 2360 | 1760 Min |
| 50CrV4 H&T | Chemical Composition % | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | Manganese | Silicon | Sulphur | Phosphorous | Chromium | Vanadium |
| 0.45 – 0.55 | 0.50 – 0.80 | 0.10 – 0.35 | 0.050 Max | 0.050 Max | 0.90 – 1.20 | 0.15 – 0.30 |






 ISO 9001:2015Brochure
ISO 9001:2015Brochure